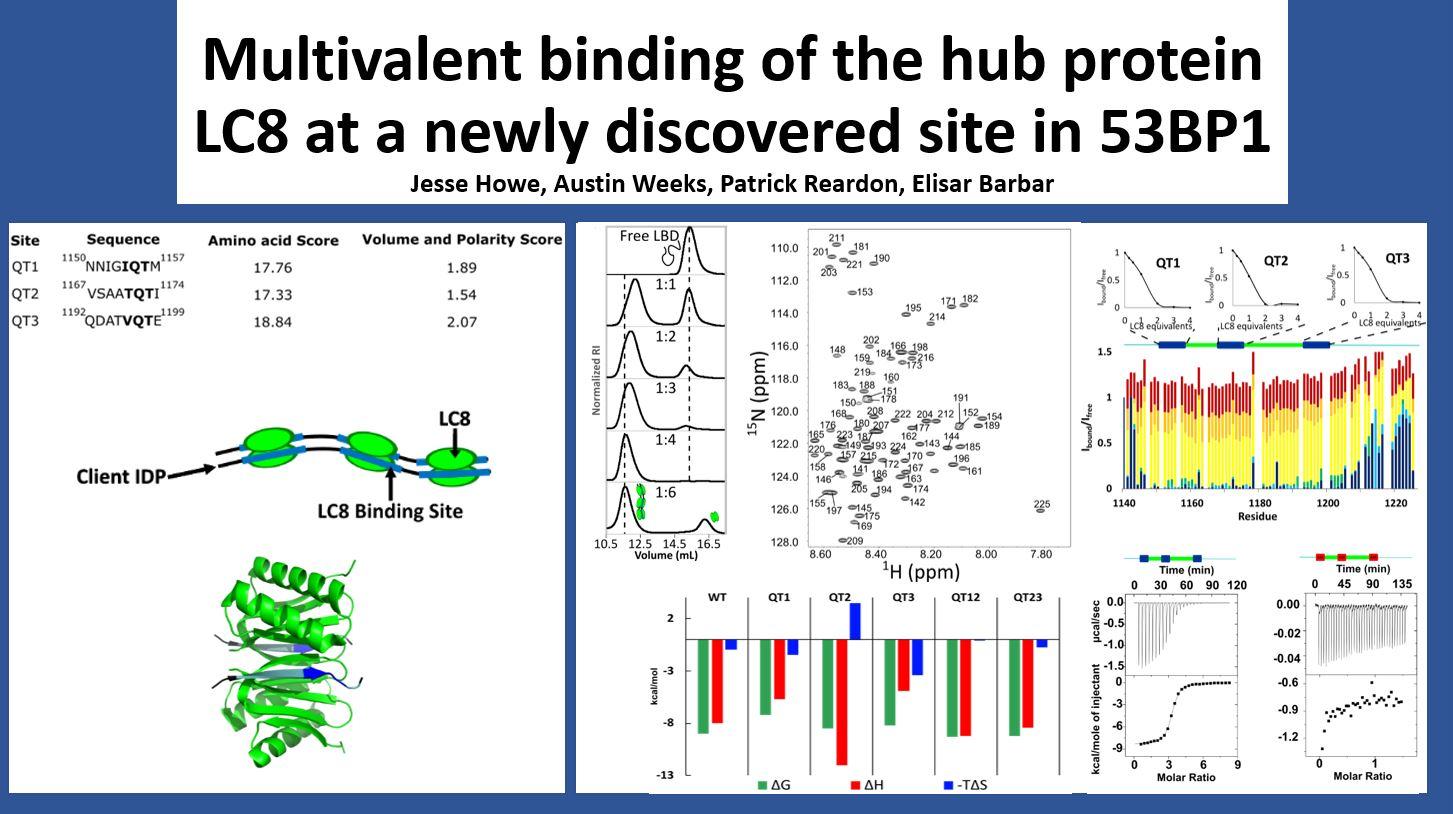
Description: 53BP1 is a key player in the DNA double strand break repair pathway. Previous literature reports only 2 LC8 binding sites in 53BP1, which are important to recruitment of 53BP1 to sites of DNA damage. Here, we report a third LC8 binding site in 53BP1 and characterize the binding of 53BP1 to LC8 using a suite of biophysical techniques.
Abstract: Tumor suppressor p53 binding protein 1 (53BP1) is a scaffolding protein involved in poly-ADP ribose polymerase inhibitor hypersensitivity in BRCA1-negative cancers. 53BP1 plays a critical role in the DNA damage response and relies on its oligomerization to create foci that promote repair of DNA double-strand breaks. Previous work shows that mutation of either the oligomerization domain or the dynein light chain 8 (LC8)-binding sites of 53BP1 results in reduced accumulation of 53BP1 at double-strand breaks. Mutation of both abolishes focus formation almost completely. Here, we show that, contrary to current literature, 53BP1 contains three LC8-binding sites, all of which are conserved in mammals. Isothermal titration calorimetry measuring binding affinity of 53BP1 variants with LC8 shows that the third LC8-binding site has a high affinity and can bind LC8 in the absence of other sites. NMR titrations confirm that the third site binds LC8 even in variants that lack the other LC8-binding sites. The third site is the closest to the oligomerization domain of 53BP1, and its discovery would challenge our current understanding of the role of LC8 in 53BP1 function.